The Microsoft .NET Framework: Its Additions to the Software World in a Wide Perspective.
The.NET Framework offers a framework that incorporates a standard code library that is necessary in the execution of computer programs. This framework includes the main elements of the code, which enable software to be fast and efficient. There are numerous programs today that are intended to make use of this common library. Consequently, software engineers will be able to use the coding capabilities offered by the.NET Framework, rather than complicate their own code.
Version 3.5 is important in the compilation and execution of programs. It provides a windows operating system based runtime environment. This system converts the programming code to machine code and is usually the core of most software applications, just as Java-based applications.
Advantages of .NET Framework 3.5
The framework is useful since it has specific advantages to both individual users and professionals. The requirement of individual users is that this system should be compatible with their software. The developers of the software would want the system to accommodate such common programming languages as C++, F#, C#, and Visual Basic. This is very convenient to both parties. Microsoft has ensured that this framework is able to use various operating systems such as Linux and windows to expand its use.
What is the reason as to why you should use .NET Framework 3.5?
The framework has been integrated in nearly all computer programs because of the advantages it provides to software developers. The common code library enables the programs to be run faster which is a significant benefit to the end-users. It even allows older software to run in your computers since it is compatible with the older versions of windows. Programs that are created prior to windows 10, 8, or 7 could be run without problems on them. Thus, it allows using the programs that are created with older code, no matter what your computer is capable of. This is why I suggest that you should install all updates on your computer.
Significant Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 Characteristics.
The most prominent aspect of the .NET Framework 3.5 is the fact that its structure is better than in the previous versions, and it addresses the problem of compatibility that was experienced in earlier versions. It solves the issues that had been encountered in the past releases. This renders the program as a necessity in all the devices. You do not have to do any extra steps to install this program provided that your windows version is running well. Nevertheless, you might have a prompt during the installation process, which requests to restart installing .NET Framework 3.5. At that, be sure to install it because a program cannot work properly without it.
At the release of Windows 8 by Microsoft the framework had four versions and was compatible with the releases. Nevertheless, older software had to be installed individually sometimes to be used by users. This version saw a major transformation because it contains the libraries of all the earlier versions and it became a staple in the computers.
System Requirements
| Workstation Operating Systems (Windows XP + Windows Vista + Windows 7 + Windows 8 + Windows 10) |
| Network Operating Systems (Windows Server 2003 + Windows Server 2008 + Windows Server 2012 + Windows Server 2019) |
| 1 GHz processor (Intel Pentium processor with minimum 400 MHz speed is required. For better performance 1 GHz processor speed is recommended.) |
| 256 MB RAM (minimum 100 MB of RAM is required for installing Net Framework. But at least 256 MB of RAM is required for proper execution.) |
| Hard Disk (Minimum 1 GB free space is required on the Hard Drive for effective execution.) |
| Graphics Card (Graphics card should provide minimum 1024×768 resolution and 32-Bit color support.) |
Supported Languages
| Arabic (ar-SA) | English (en-US) | Hungarian (hu-HU) | Portuguese (pt-BR) |
| Chinese (zh-CN) | Finnish (fi-FI) | Italian (it-IT) | Portuguese (pt-PT) |
| Chinese (zh-TW) | French (fr-FR) | Japanese (ja-JP) | Russian (ru-RU) |
| Czech (cs-CZ) | German (de-DE) | Korean (ko-KR) | Spanish (es-ES) |
| Danish (da-DK) | Greek (el-GR) | Norwegian (nb-NO) | Swedish (sv-SE) |
| Dutch (nl-NL) | Hebrew (he-IL) | Polish (pl-PL) | Turkish (tr-TR) |
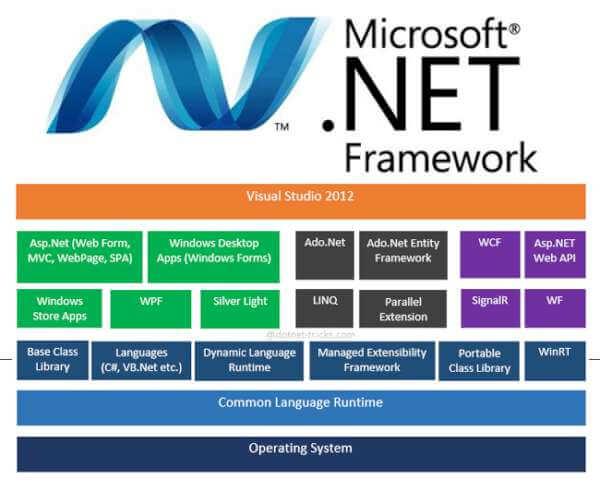
Library Components
| LINQ | SQL | XML | AJAX |
| ASP.NET | JSON | REST | POX |
| RSS | ATOM | WCF | WF |
| WPF | BCL | * | * |

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.